
Verbs can also be divided into various groups. Any action, occurrence, or condition of being is described by a verb. One of a sentence's most crucial parts is the verb. The subjects and objects of phrases are nouns.

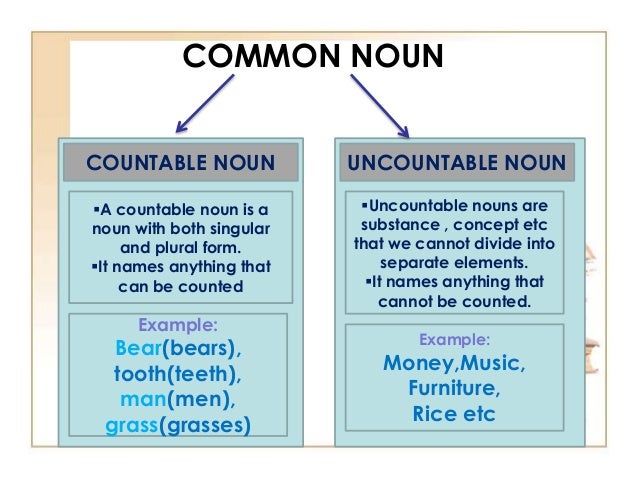
Individuals (a girl, a baby, a teacher), objects (a seat, a marker, a laptop), places (Milan, a clinic, a yard), animals (a wolf, a koala, a dog), and substances (lumber, glass, plastic) are all examples of nouns. They are eight parts of speech in English (those who have comparable functions within the syntactical structure of sentences). When syllables are categorized as falling to the identical part of speech, they frequently display similar grammatical behaviour in that they experience inflexion for comparable properties, as well as similar syntactic behaviour on occasion. Because open and closed classes vary from language to language, they are not fixed.Ī group of words (or, more broadly, of lexical items) with related linguistic characteristics is referred to as a component of speech. Word classification is essential in languages because it enhances knowledge of a language's grammatical framework. Closed classes, like pronouns and conjunctions, only occasionally add new members in contrast to open classes, which typically include nouns, verbs, and adjectives. There are two types of word classes: open and closed. Even though the term "form class" has several ambiguous definitions, it is still frequently used. Some writers limit the term "lexical category" to only one specific type of noun phrase for them, it does not include words that are regarded as function words, like pronouns. The art of speech includes word class, lexical class, and lexical category-particularly in discourse analysis classifications, which frequently make more exact distinctions than the conventional scheme does.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
